Take out a piece of paper, and write down what you think makes your company different from its competitors. Now, Google your competitors and see if you can tell the difference between what you wrote, and how they describe themselves. If it sounds the same, keep reading.
Let’s say you’re the CEO of a fortune 500 company looking for some advice. Two top tier global consulting firms are recommended, and based on their website descriptions of “Who They Are” which one would you chose?

Can’t decide? That’s the challenge I’m talking about. Although one firm uses “advisors”, they are describing what the firms do, not who they are, and as you can see, the sound the same. If some of the smartest guys in the business are getting it wrong, and they’re the “advisors to the world’s leading businesses” you shouldn’t feel bad.
Why is it so hard? There are two key reasons; the first being in B2B, we are conditioned to think that what we do is who we are. It’s the Achilles heel of effective marketing communications, the bad habit of over communicating and focusing what you sell (what you do) versus who you are (what makes you different).
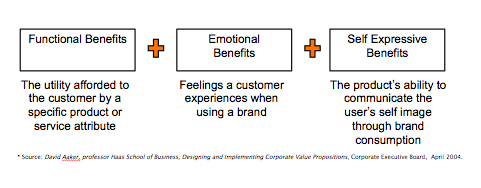
Making things worse is when B2B marketers talk about the value of what their company does, they use terms associated with business value, the functional benefit or business outcome of the product or service being sold (e.g. increase revenue, reduce cost, retain customers, etc.). It’s non-differentiating because competitors use the same language, and that’s the second major challenge to overcome.
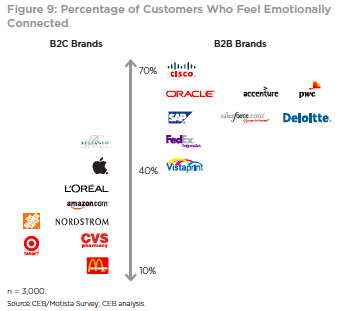
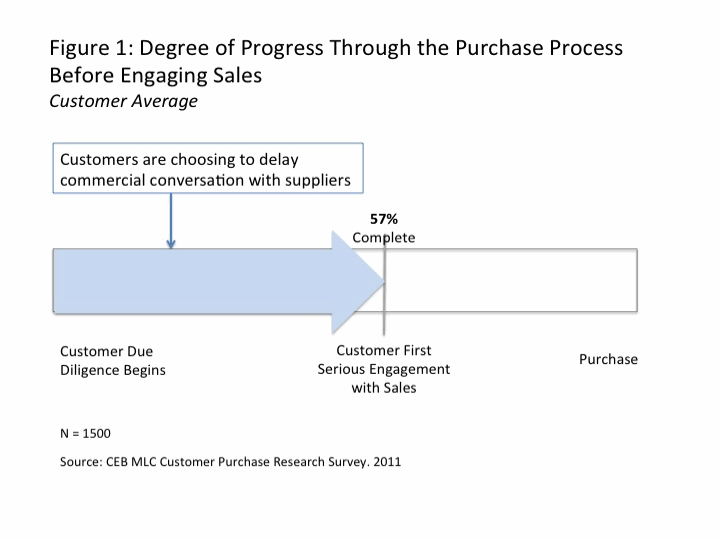
Over the years, marketing communication has evolved from talking about how great the company was to talking about what it does for customers. Thankfully the “we’re number 1” days are over but unfortunately, the “what we do for customers” has been defined by what the company sells. It is time to evolve again and speak to more about the “DNA” of the organization. Research from CEB has shown that buyers figure out what companies sell (what you do) relatively quickly. It takes them much longer to figure out why they should buy from one company or another.
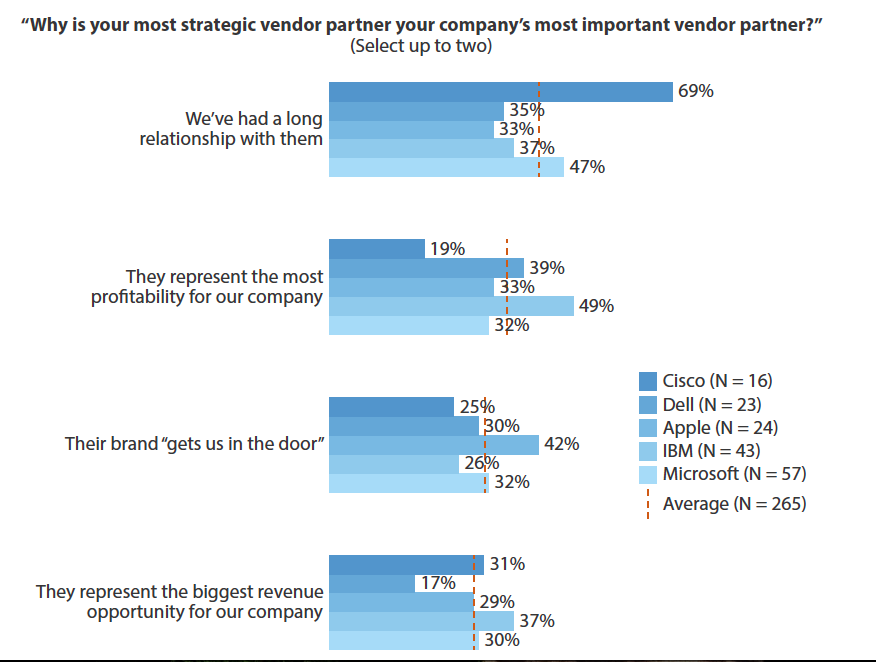
And surprisingly, when they do make the decision, it often has little to do with “business value” of the product or service itself, and more to do with the emotional connection they feel to it, or to your brand. Buyers are not the rational beings we once thought, they do business with businesses for very personal reason, according to the CEB research. As a result, they want to get to know the company as well as they know the product or service.
So, how do you “humanize” the company? Here are some tips to get your started:
- Ask customers – sounds obvious, but rarely happens. Ask them why they do business with your organization and others. You might be surprised by what you’ll learn; it may have nothing to do with your products or services. Use this information to communicate back to them “who you are” in the language and context that is meaningful to them.
- Survey employees – this may help uncover why the organization can’t get on the same page when it comes to defining the company. Employees have a tendency to define the company and what it does, based on their own experience with the products they know, and customers they serve. As a result, they have a myopic view of the organization. You will find multiple views on your value, and the type of company you are, across your organization.
- Decide on the type of company you are – pick up a copy of Michael Treacy’s Discipline of Market Leaders. In it, Treacy and Fred Wiersema define three value proposition types based on business models; Operational Excellence, Product Leadership, and Customer Intimacy. Use this framework as a starting point to define your organization and its’ language. It also helps get everyone on the same page.
- Create a persona – once you have consensus on the type of organization and its value to customers, it is time to figure how to differentiate it. In this step, use brand archetypes to help define the company persona. Here’s a free list of 40 archetypes. Create a working session and have the group discuss how the company views the world, how it reacts to bad or good news, how it speaks — what is the tone? Keep the conversation away from what the company makes or does, and on the organization itself.
Buyers have changed. They want to know who you are, because they already know what you do. And they’re looking for a little of themselves in your brand. Relate to them on a human level. Tell them who you are in a way that connects with them. If you do, it will differentiated you, because like people, no two organizations are exactly alike.